Key Takeaways
- Understanding the saving and investing resources available to you will allow you to be efficient with your retirement planning.
- Detailed income and expense analysis prior to and during retirement will allow you to make adjustments along the way and avoid compounding mistakes.
- Be open to help, whether from family, friends, resource groups or professionals like financial advisors or CPAs.
Retirement is expensive. Experts estimate that you will need 70 to 90 percent of your pre-retirement income to maintain your standard of living when you stop working. For most retirees, you will need to plan for 25 to 30 years of retirement income, over which time many expenses will rise and you will need your income to grow to keep pace with inflation.
Social Security benefits will replace only about 40% of a retiree’s income on average. High earners should expect Social Security to replace substantially less of their retirement income.
According to the U.S. Department of Labor, fewer than half of Americans have calculated how much they need to save for retirement. Pensions are a rarity for most private sector employees and just 44% of workers participate in a defined contribution plan, such as a 401(k).
These are just some of the factors that have created what many see as a pending crisis in American retirement. To give yourself an edge, start planning and saving early. Start small if necessary and increase the amount as you’re able.
Retirement planning is a process that, ideally, lasts for decades from your first early career retirement plan contribution to savings withdrawals in later life. Some people get a late start to saving and may need to make trade-offs such as downsizing, retiring later or working during retirement. Take advantage of online financial calculators and government resources to develop a personalized retirement plan.
When To Start Planning for Retirement
The time to start planning for retirement is now. If you are in the workforce, it’s never too early or too late to plan for retirement.
As you make your plans, keep these questions in mind:
- At what age do you hope to retire?
- What do you plan to do in retirement?
- How many years do you think you’ll live after you retire?
- What are your planned sources of retirement income?
- How long do you have to save?
- How are you going to account for risks, including inflation?
- Are you willing to make changes to your retirement age, income or lifestyle to make retirement a reality?
Setting goals is the first step in building your retirement plan. Put them in writing and revisit them from time to time. Focus on what you can control and how much you need to save.
The planning strategies you implement depend on your career stage, your financial goals, when you would like to retire and your current financial situation. If, for example, you are a late-career professional who hasn’t saved enough to fund your retirement, consider factors such as time horizon and risk tolerance, both of which affect the types of investments that make sense for you.
Time horizon is the period of time over which investing takes place. Short-term investments have time horizons of fewer than three years. If you plan on retiring in 20 years, your retirement planning would have a time horizon of 20 years. Nevertheless, a significant portion of your investments may require a longer time horizon. Even though you’ll require retirement income to commence in 20 years, it must also sustain for a potential additional 30 years thereafter.
Risk tolerance refers to the level of market risk you’re willing to take. For example, stocks carry higher risks than bonds, but stocks have more growth potential. Your risk tolerance will impact how your investment portfolio is constructed. The overall mixture of stocks, bonds and cash within your various accounts is referred to as your asset allocation.
Key Planning Questions: Will You Have Enough Income in Retirement?
- What Is Your Estimated Monthly Retirement Income?
Calculating this number may depend on how you wish to withdraw your income and what sources of income you have. Pensions or annuities may offer a higher rate of return than simply withdrawing from a retirement account. It is also important to consider what you will receive in gross income vs net income after taxes.
- What Are Your Anticipated Monthly Income Expenses in Retirement?
Retirement expenses are the biggest factor in determining retirement planning success. Large essential expenses such as a mortgage or other debt can be difficult to manage on a fixed income in retirement. Planning ahead to limit your required expenses can make executing a plan easier.
Making a Budget
Any retirement plan should include a budget that outlines realistic expenses and income expectations.
To start your budget, collect your last couple months or so of bank account and credit card statements to organize your expenses. Categorize your spending by food, clothes, housing, transportation, health care, entertainment, etc.
Don’t forget your routine costs, such as property taxes, auto insurance, car registration fees and driver’s license renewals. Also, remember nonroutine expenses such as gifts and the costs of hobbies and vacations.
If you use or have access to budgeting software , it can be a helpful organizational tool for your planning. Budgeting software can pull electronic records from the past and help you group them by cost type. Even if you can’t find all your expense records going back a full year, tracking a few months of expenses can get you the data you need to extrapolate a yearly estimate.
Establishing a budget can be beneficial for two reasons. First, it may help you realize where you can tighten up your spending today to boost your retirement savings for the future. Second, it should give you a better idea of what you will be spending money on in retirement and what you won’t.
For instance, daily transportation costs may fall when you aren’t commuting to work. Food costs may go down when you have more time to cook for yourself. Alternatively, travel costs may rise, especially in the early years of retirement, when you will be traveling more often or on more lavish trips.
- Plan for Emergencies
- Incorporate some savings cushion for things like home and car repairs, unexpected medical costs and family emergencies.
- Add Up Your assets
- Get the most recent statements from any 401(k), IRA and other investments and savings.
- Estimate Income
- Incorporate expected pension income into your calculations. Moreover, you can estimate your Social Security income online. Also, remember to include any annuity income in your assessments.
- Remember Inflation
- As you prepare your budget, consult the Bureau of Labor Statistics for current and historical inflation rates, and account for it in your projections.
- Estimate Investment Earnings
- Determine the average rate of return expected on your investments.
- Use Tools You’re Comfortable With
- If you like writing on paper, use paper. If spreadsheets or computer documents are your thing, go that route. Don’t let the method get in the way of planning.
Start Your Budget
It’s especially important to make sure you include health care costs. If you plan to retire before you’re eligible for Medicare at age 65, make sure to include the cost of health insurance your employer will no longer be funding. Try to project other health care costs, such as copays, long-term care and dental expenses that are not covered by Medicare.
Once you have a breakdown of your expenses, identify your sources of retirement income and compare the expenses to your expected income. Review the national average retirement income to assess the health of your finances.
Retirement Planning Tools
Take advantage of the retirement planning tools available online to prepare for your golden years. These tools can help you estimate how much you need to save, what kind of income you can expect and what resources are available to get you to a strong position.
For example, the federal government offers a retirement page that includes tips about Social Security, federal and private pensions, civil service and retirement savings.
Other government-sponsored and nonprofit online retirement planning tools offer guidance on monitoring financial health, early and late retirement, retirement plan laws and maintaining your lifestyle in retirement.
FINRA
The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates brokerage firms and the sale of securities, such as stocks and bonds. In addition, FINRA works to educate investors through a variety of resources, including retirement planning tools.
Social Security Administration
The Social Security Administration is a government program established to provide financial protection to Americans through benefits programs, including a retirement program.
- Retirement calculator
- Life expectancy calculator
- Spousal benefits calculator
- Online benefits planner
Consumer Financial Protection Bureau
As part of its efforts to “empower, enforce, and educate,” the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau promotes financial literacy through a variety of resources, including a Social Security benefits calculator and articles about retirement payout options, pensions and debt management.
U.S. Department of Labor
The Labor Department protects the welfare of American workers and retirees. Among the department’s chief responsibilities is educating retirement plan participants about their rights under federal law.
Other Tools and Resources
If you haven’t found what you are looking for elsewhere, there are many retirement and investment companies that offer free or limited tools for investors and retirees. Wherever you have your retirement accounts, there will likely be an accessible retirement planning tool that you can use to model an income plan. If your broker or retirement provider doesn’t offer those tools, many larger discount brokers offer free tools that you can use without the use of a login, and many are accessible without a fee.
When it comes to mapping out a focused retirement plan, it is worthwhile to get a second pair of eyes on your expenses, income plan and future assumptions. A fiduciary financial advisor helps people plan for retirement and can offer key insights on gaps, considerations or risks you may have missed.
Saving for Retirement
As you participate in the workforce as an adult, retirement will always be on the horizon, drawing closer at each stage of your career, shortening the time horizon of your investments. This can be intimidating, especially later in your work life.
Ideally, you’ll have started planning and saving for retirement when you were young, but it’s never too late to improve your outlook for retirement. Don’t let the fact that you haven’t planned yet — or planned adequately — keep you from addressing retirement now.
As experts at the Center for Retirement Research have noted, retirement “is not a linear process.” Often, regular expenses like mortgages and college tuition cost more than we expect, and life events like divorce and medical emergencies force many to “start all over again.”
The researchers also noted that pre-retirees can be immobilized by things that affect their emotions. They can become angry at their boss or the government and experience anxiety over their investment decisions.
The best way to overcome this is to focus on the things you can control. Sometimes baby steps are the only way to move forward. But as long as you are making progress, you are improving your chances of success.
Starting in Your 20s and 30s: Early-Career Planning
Your early career is the ideal time to start saving and making it a habit. Set aside a little of each paycheck before you get used to having the full amount at your disposal.
When you become financially independent and support yourself on your career earnings alone, create a budget that includes retirement savings. You don’t have to be able to max out your retirement accounts in order to start, you can start small.
This is a time to become comfortable with your finances and learn about the opportunities and financial tools available to you. People who are motivated to be financially literate are generally better able to handle money and less likely to run into problems. No one is born understanding how money and finances work. Don’t let your perceived lack of knowledge (or overconfidence) hold you back from learning more about managing your finances.
Participate in your employer’s retirement savings plan. At minimum, the automatic payroll deductions will make saving easier, and you will receive a tax benefit from saving pretax funds. Also, if your employer offers matching funds, take advantage of them. Do not leave free money on the table.
This is also a good time to establish a pattern of living within your means and of avoiding the temptation to buy more as you earn more. Creating structure around your income and spending can protect your money from “lifestyle creep” or the increase in expenses that can come from earning more. Many retirement plans offer the ability to automatically increase your contributions by a certain percentage each year. If you expect yearly raises, it can be a good time to set your annual increase.
The earlier you start saving and investing, the more time your money will have to accumulate and compound. Compounding is key here. This means that your interest will earn interest and then that interest will earn interest and so on with every passing year. This increases the chances of you enjoying a comfortable retirement. It also decreases the amount you will need to save every year. In time, with patience, your money will out earn the amount you could save from your income alone.
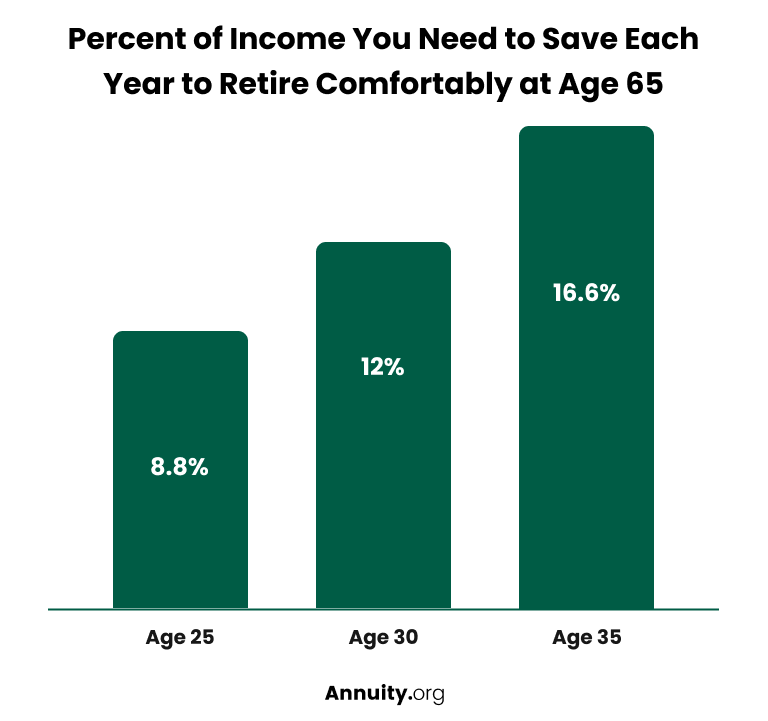
Wade Pfau, professor of retirement income at the American College told Money.com that a worker who starts saving at age 35 will have to put away 16.6% of their income for 30 years to retire comfortably at age 65. If the same worker starts saving at 30, the requirement drops to 12%. At age 25, just 8.8% — including the company match — must be saved every year until age 65.
The longer you wait, the larger your savings burden becomes. Using a rate of return of 10%, the table below shows how much you need to save to retire as a millionaire at age 65.
| Age | Savings Rate |
| 20 | $116 per month |
| 30 | $307 per month |
| 40 | $847 per month |
| 50 | $2,623 per month |
Starting in Your 40s and Early 50s: Mid-Career Planning
As you enter mid-career, keep revisiting and building on your retirement plan. Start to envision how you’d like to spend your retirement years. These tend to be your peak earning years, so do whatever you can to increase your earnings and retirement savings.
If you haven’t started saving, start as soon as possible. When you can, increase the amount you save. Keep track of your investments to make sure they’re allowing you to reach the goals you have set, and consult with a professional investment advisor or retirement planner to make sure you’re on track.
Look for opportunities to increase your savings. For example, when your children leave the home, your spending should decrease. Yet a study by the Center for Retirement Research found that, in spite of the fact that people at this stage of life are less likely to have mortgage payments, households increase contributions to 401(k) plans by only 0.3% to 0.7% when the kids leave home.
Now is also the time to consider the effects of committing, or recommitting, yourself to a healthy lifestyle for the benefit of your health care costs in retirement. The Aegon Retirement Readiness Survey 2021 concluded that “Leading a healthy lifestyle is perhaps the best backup plan especially during a pandemic and a significant factor in preparing for a comfortable and active retirement.”
Starting in Your 50s and Early 60s: Late-Career Planning
Ideally at this point, you’ve been preparing for retirement and have saved as much as possible. For many, though, retirement seems to sneak up; other priorities have gotten in the way of their retirement planning.
There’s still time to fund a comfortable retirement if you focus on making the most of the time you have left.
When you’re 50 or older, you’re allowed to make extra deposits to retirement savings plans, known as “catch-up contributions.” These contributions have the same tax advantages as your ordinary deposits. In 2023, 401(k) accounts allow an additional $7,500 for a total allowable contribution of $30,000. IRAs, both Traditional and Roth, allow an additional $1,000, for a total of $7,500.
If you’re really behind, you may have to consider working longer than you’d planned. If you stay in the workforce until age 70, you will maximize your monthly payments from Social Security. This also gives you more time to save and for your savings to build.
After you retire, you might consider taking a part-time job to supplement your savings. Even a little extra income can improve a retirement plan substantially by lowering the amount of money you need to withdraw. For example, making $12,000 a year in part-time income means an additional $12,000 can remain in your retirement accounts to continue growing. On a $500,000 retirement portfolio, that is the difference between a 6% withdrawal rate ($32,000) and a 4% withdrawal rate ($20,000).
Moreover, examine any financial help you are giving to your adult children. Try to minimize that to ensure both that they are financially independent and that you are better positioned for retirement. Forty-three percent of parents responding to a survey in 2022 reported risking their retirement security to provide financial assistance to their adult children.
Start reducing your debt, starting with the highest interest rates first. If you have a mortgage, consider whether your interest rate is high enough to make extra payments worth it. Every dollar you spend, save or use to pay down debt has an opportunity cost because it is not able to go somewhere else. If you expect to make 5 to 8% in the market annually over the next decade, but you only pay 3% on your mortgage, it does not make financial sense to pay extra toward your mortgage.
If you live in a large house, or have a separate dwelling, consider whether you can monetize this space better. While interest rates in the past made it easy to sell or move, present mortgage rates may make moving difficult unless you can avoid a loan. Selling your home and buying something smaller can be a viable strategy to reduce debt, but only if it will free up money for better retirement saving.
Take a serious look at your retirement portfolio to make sure it’s on target. Update your retirement budget and adjust your investment strategy as necessary. If you find you aren’t meeting your goals, there are three options to improve your plan:
- Save more
- Invest better
- Retire Later
Read More: Essential Retirement Statistics for 2023
Timeline of Retirement Benefits
- Age 59 1/2: You may start making withdrawals without penalties for early distributions.
- Age 62: You are eligible to receive reduced Social Security benefits. But if you wait longer, your monthly benefit will be higher.
- Age 65: You are eligible to receive Medicare. Make sure you apply for those benefits in the three months before your 65th birthday.
- Between ages 66 and 67: You are eligible for full Social Security benefits.
- Age 70: Maximum monthly Social Security benefits begin.
- Age 73: You must begin taking required minimum distributions.
Source: U.S. Department of Labor
Think about how you want to spend your time in retirement. Where do you want to live? Do you plan to work part-time? Do you hope to be near family? Will you travel? Do you have any hobbies? What do they cost? These questions will help keep you on track.







