What Is a Certificate of Deposit?
A certificate of deposit (CD) is a savings vehicle that provides interest compensation in exchange for a commitment to leave the amount invested on deposit, or in a bank account, for a predetermined amount of time. Early withdrawal typically results in a loss-of-interest penalty. While rare, some CDs impose particularly burdensome penalties that can result in loss of principal, or the original sum of money put into the investment.
CDs are structured for various lengths of time, with most spanning anywhere from one month to five years. They can reflect fixed-rate or variable-rate terms, but fixed arrangements are, by far, the most prevalent. Generally, the longer the term, the higher the interest rate offered — provided all other variables remain the same.
Deposit requirements vary but can be as low as a few hundred dollars. Typically, rate offerings are staggered, with higher deposit amounts garnering higher rates of interest, (if all other factors remain constant).
Regardless of the specific terms, CDs are broadly popular with investors that value high-quality, stable-value, interest-bearing vehicles, but can afford to lock up their money for a period. Understanding when and how to use CDs to achieve financial goals is a key piece of financial literacy.
How Does a CD Work?
The process for investing in a CD begins the same way as the opening of a traditional checking or savings account. You are required to apply online or in-person with the issuing financial institution. A primary difference is that the initial deposit into a CD is generally the only one you will make, while a traditional bank account allows for periodic deposits.
Another key difference relates to the specific terms and conditions associated with a CD, such as maturity date, interest rate and early withdrawal penalty. The maturity date is the date the investor is allowed to withdraw money from the CD.
How Are CD Rates Calculated?
CD rates are the interest rate banks pay you for letting them hold your money. The rates can vary from bank to bank and are usually affected by three factors:
- The term of the CD (how long you must leave your money in the CD before it matures).
- Prevailing interest rates.
- How much the bank expects to earn on the money you deposited.
You should take all these factors into account — along with your initial deposit — when calculating the return on your investment in a CD.
For illustrative purposes, consider the following example:
- A $10,000 CD investment is made on Jan. 1, 2021.
- The term is two years (maturity on Jan. 1, 2023).
- The nominal rate, or stated annual rate, is 2.5 percent, with daily compounding of interest.
- The early withdrawal penalty amounts to six months of interest, which approximates $125.
$10,000 × .025 ÷ 12 × 6 = $125
Incidentally, the nominal rate of 2.5 percent reflects an annual percentage yield (APY) of 2.53 percent. The APY, which is also referred to as the effective annual rate, reflects the effect of compound interest. The computation is below.

Given these terms, at the end of the two-year period, the investor can expect to receive the following proceeds from the initial $10,000 investment:
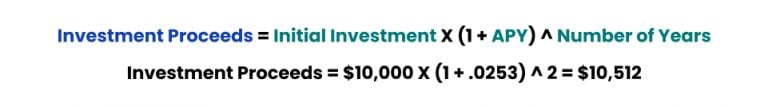
Read More: Will CD Rates Go Up?
What Are the Different Terms for CDs?
CD Terms are the length of time your money is invested in a certificate of deposit. Typically, when you purchase a CD, you agree to keep your money in it for a specific period of time.
- Short-term CDs
- These typically range from a few months to a year. They are best suited to save money for something you plan to pay for in the near future — a vacation, wedding or down payment on a car.
- Mid-range CDs
- The terms on a mid-range CD are typically between one and three years. These may be a good choice if you are saving toward a project at least two years in the future.
- Long-term CDs
- Long-term CDs typically have terms of four, five or even 10 years. These are best suited for costs you expect in the distant future.
Common CD Term Ranges
The rate you receive for a CD is usually related to its term. Shorter term CDs tend to have lower rates, while longer term CDs pay a higher rate.
What Happens to Your CD at Maturity?
When your CD matures — reaches the end of its term — you typically have a grace period to decide what to do with it. This grace period is relatively short — one or two weeks in most cases — so it’s wise to make up your mind well before your CD reaches maturity.
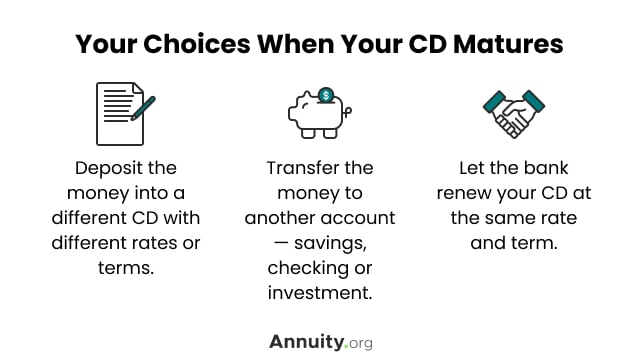
Before deciding, you should compare rates, terms and whether you have a better option at receiving a higher return on your money.
What Are the Types of CDs?
The most common CD variations, are outlined below.
- No-penalty CD
- This structure allows for penalty-free early withdrawal; it is typically paired with a relatively low interest rate.
- Jumbo CD
- A jumbo is structured the same as a standard CD, but it entails a higher initial deposit; sometimes as much as $100,000 or more. In return, a jumbo will generally offer a comparatively high interest rate.
- Bump-up CD
- This structure allows you to request a higher rate if prevailing marketplace conditions warrant it. Typically, only a single request is permitted, but some longer-term CDs allow for multiple requests.
- Step-up CD
- A step-up option provides for specified rate increases administered by the issuing institution at periodic intervals. For example, the rate on a 36-month step-up CD might be scheduled to increase every six months.
- IRA CD
- This is essentially a regular CD that has been designated to be held in a tax-advantaged individual retirement account (IRA).
What Are the Pros and Cons of CDs?
It’s important to consider all aspects of certificates of deposit to determine if it’s the right investment option for you. Here is a high-level list of pros and cons that may help you decide.
Pros & Cons of CDs
Pros
- Very safe investment with zero credit risk below insured limits.
- Stable value product with zero volatility (unlike stocks, bonds, and alternative investments).
- Can offer a more competitive rate than other types of short-term investments.
- Can facilitate disciplined savings behavior for individuals inclined to spend cash.
- Relatively easy to establish with an array of traditional and online options available.
Cons
- Entails a lockup period and an early withdrawal penalty.
- Interest rate earned often fails to keep pace with inflation, which erodes purchasing power.
- Relatively inferior option for longer-term investment horizons.
- Accrual basis taxation on interest earned does not align with cash inflow.
- Auto renewal feature can be problematic.
Read More: Opening a CD for a Child
Are CDs Safe?
On the surface, CDs are one of the safest, most stable investments you can make. However, it’s important to be cognizant of the unique risks associated with this type of instrument. The most prominent considerations are outlined below.
Are CDs FDIC Insured?
A properly structured CD is fully ensured up to $250,000 for an individual account and $500,000 for a joint account. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) provides insurance for CDs issued by banks, and the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) provides insurance for CDs issued by credit unions (via the National Credit Union Share Insurance Fund).
Above the insured limits, loss of capital is possible, but the risk is fairly remote for CDs issued by financially sound institutions. It can increase significantly for CDs issued by poorly capitalized institutions.
Inflation Risk Exposure
While credit risk is remote, a notable exposure for some CDs is inflation risk. This is particularly worrisome for longer-term products, with maturities extending up to and beyond five years. For these instruments, a substantial uptick in inflation can quickly overshadow the interest income offered, leaving an investor with less real wealth at maturity.
Liquidity Risk
Another pertinent exposure, oftentimes the greatest, is liquidity risk. A CD requires you to lock up your money for a stipulated period. If you violate this requirement and redeem your funds early, you will face an early withdrawal penalty. The penalty usually equates to a certain number of months of interest (like the six months of interest specified in the example above). However, some CDs impose especially onerous penalties that can result in loss of principal.
Is a CD Right for Me?
Whether or not a CD is a sensible investment for you is highly dependent on your tolerance for risk, which is a function of your near-term liquidity needs, appetite for volatility and investing time horizon. In the right situation, a CD can provide an excellent complement to a portfolio of cash and longer-term investments, such as stocks, bonds and alternative investments.
Read More: Investing for Beginners
When Does a CD Make Sense?
If you have a relatively short investing time horizon and can comfortably lock up your money, then a CD could be sensible. If you have a very low tolerance for volatility, a CD makes even more sense. However, before you invest in a CD, be sure to evaluate the wealth-eroding effect inflation can have on your money, especially if you are entertaining longer-term products.
When Doesn’t a CD Make Sense?
If you have erratic, near-term liquidity needs and may require immediate access to your money, a CD is not appropriate. Additionally, if you have a relatively long investment horizon, such as the accumulation period prior to retirement or the spend-down period during retirement, a CD is not a great option. For you, investing in some combination of stocks, bonds, alternative investments, and annuities, offers a much more rewarding risk/return profile, with higher growth and/or income potential.
Is a CD Sensible for Retirement?
On an absolute basis, a CD investment is not advisable for someone with a long-term investing horizon, such as retirement. However, it can make sense for an investor with a segmented, or goals-based, approach to investing.
For instance, assume a long-term investor has thoughtfully assigned his liquidity needs into the following buckets:
- Known spend in zero to six months
- Likely spend in six to 12 months
- Potential spend in one to two years
- Potential spend beyond two years
In this scenario, a CD investment could be sensible for the six to 12-month bucket. Let’s expound.
Assume Jim has a life situation that calls for him to hold 12 months of living expenses ($50,000) in liquid, stable-value assets. Jim has that much saved, but he doesn’t want to simply store the cash in his savings account, which yields zero. So, he has carefully thought about things and determined, in a worst-case scenario, he will only need half the annual estimate within the next six months.
This analysis prompts Jim to invest $25,000 in a one-year CD at one percent. In doing so, he has prudently carved out the less time-sensitive half of his $50,000 liquidity cushion and optimized his financial position. This type of strategic, time-based investing is a prime example of how a CD can make sense in a long-term portfolio.
Other Important Considerations
In addition to weighing your risk tolerance, you will want to consider the tax treatment of CDs as well as the institution’s automatic renewal policy when deciding whether to invest in a CD.
Taxation
When you open a CD, the money you invest and the interest it earns is locked up until the maturity date. However, the issuing institution periodically applies interest to your account and reports it at regular intervals, usually via a monthly or quarterly statement. As this interest is reported, it is taxable. So, while you won’t receive any of the funds until the CD matures, you are liable for the income tax on any accrued interest.
Read More: Federal Tax Brackets
Automatic Renewal
Unless you specify otherwise, once a CD matures most institutions will automatically renew it at the prevailing interest rate, following a specified grace period. This might not be in your best interest. You may need the funds, or alternatively, you may be able to invest them in a higher-yielding CD with another institution. Therefore, it’s important to keep the CD maturity date on your radar. If you want to redeem the funds, you will need to provide formal notice to the issuing institution.
Where Can You Get a CD?
Certificates of deposit can be purchased through most banks, credit unions, brokerage firms and similar financial institutions.
- Banks
- You can shop for certificates at both traditional brick-and-mortar banks or online banks. Online banks tend to offer better rates on CDs and other accounts than traditional national banks. This is because online banks don’t have the same expenses as traditional banks.
- Credit Unions
- Credit unions are similar to banks. A major difference is that credit unions are customer-owned, and their accounts — including CDs — may offer higher rates than banks. Like banks, most credit unions are federally insured.
- Brokerages
- The biggest difference between bank or credit union CDs and brokered CDs is that you can get out of a brokered CD by selling it on the secondary market — similar to how you would sell a stock or bond.
Where to Buy CDs
Regardless of where you purchase a CD, you should compare rates, terms and fees before deciding if a CD is the best investment for you.
CDs vs. Other Types of Savings Accounts
Savings accounts give you greater flexibility over making withdrawals while CDs may charge penalties if you take money out of your account early. On the other hand, CDs tend to offer higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts.
When to Choose: Savings Account vs. CDs
| Savings Account | Certificate of Deposit |
|---|---|
| Choose a savings account if you are creating an emergency fund or if you need to dip into your savings from time to time. This will keep you from having to pay early withdrawal penalties with a CD. Also consider a high-yield savings account to maximize your interest if the terms fit your needs. | CDs tend to have higher returns than savings accounts. If you can set your money aside without touching it for the term of the CD, you’ll likely make more money than in a savings account. CDs are typically better if you are putting the money aside for a specific goal for that money. |
Let’s Talk About Your Financial Goals.
Alternatives to CDs
On the shorter end of the maturity spectrum, CDs are comparable to other high-quality instruments, such as U.S. Treasury bills, commercial paper and money market funds, which comprise an assortment of other assets, including CDs. CDs are generally less liquid than the other instruments but investors are compensated for this via comparatively higher interest rates.
Another highly liquid alternative is a high-yield savings account, which is typically offered by online banks. The absence of a traditional, brick-and-mortar overhead structure can make these vehicles quite competitive from a yield perspective. However, unlike a fixed-rate CD, the rate on a high-yield savings account can change at any time.
CDs vs. Annuities
Consumers who are looking for a low-risk alternative to CDs may consider a fixed annuity, specifically a multi-year guaranteed annuity (MYGA), as an option.
Both products lock up a lump sum and allow it to accumulate interest over a set period. And each guarantees a rate of return and offers principal preservation.
However, comparing CDs to annuities is not apples-to-apples. CDs are generally a short-term investment, while annuities are not. Other differences include the tax advantages and death benefits that are available with annuities but not with CDs.
A qualified financial advisor can guide you through the similarities and differences between annuities and CDs and help you pick the product that best fits your needs.
CDs vs. Other Investments
When considering how to invest your money, it is important to understand how different investment vehicles work, what their purpose is and what your goal for investing is.
CDs are a savings account. They return a modest yield for the investment. Even long-term CDs may have a relatively short life span compared to investments designed to provide retirement savings or income.
- CDs vs. Money Market Accounts
- CDs tend to have higher rates of return than money market accounts. But a money market account will give you greater access to your money if you need it — allowing withdrawals up to six times a month. They key differences are access, checking-account-type qualities and the option to regularly withdraw money.
- CDs vs. IRAs
- An IRA is a retirement account. It gives you tax advantages to save for retirement and has stiff penalties if you withdraw money prior to retirement. You can contribute money to an IRA every year up to IRS limits. A CD is a savings account. It does not provide the same tax advantages as an IRA, but it allows you to withdraw money when it matures.
- CDs vs. Bonds
- CDs and bonds have several similarities. Both are a type of “safe-haven” investment, provide little risk of loss and offer relatively small returns on the original investment. But they behave differently depending on interest rates. Bonds tend to provide higher returns when interest rates are low, CDs provide better returns when interest rates are high.
CDs Compared to Other Investments
CD Strategies
There are several strategies to get the most return out of investing in certificates of deposit. These largely deal with leveling out the effects of changing interest rates while your money is tied up in a CD to maximize your eventual return.
The ladder and barbell strategies are designed for higher rates over time while the bullet strategy shoots for a future spending goal.
CD Ladder Strategy
A CD ladder requires you to buy several CDs, each at the same price but with staggered terms. Each time one of your CDs matures, you reinvest the money in a long-term CD.
The strategy gets its name because each CD is like a rung of a ladder.
For example, let’s say you start with a $5,000 investment. by putting $1,000 into five different CDs — a one, two, three, four and five-year CD. Each time one matures, you reinvest the money into a five-year CD.
At the end of five years, you now have a five-year CD maturing every year.
The benefit is that if you ever need the money from your investment, you can cash out within a year. Invest in shorter-term CDs and you can have quicker access to your money — but the rates will be lower.
CD Bullet Strategy
With the bullet strategy, you purchase multiple CDs over time. Each one has a progressively shorter term, but all of them timed to mature on the same date.
Rather than reinvesting, as you do with the ladder strategy, the bullet strategy aims to hit a target for a major purchase or other spending goal.
This strategy can work to pay for a new car, a down payment on a house or a wedding.
CD Barbell Strategy
The barbell strategy allows you to measure your investment against changing rates. It works by dividing your investments into short-term — such as six-month CDs— and long-term CDs. But you avoid mid-range CDs.
When the short-term CDs mature, you compare market rates. If rates have gone up, you move the money to long-term CDs. If the rates haven’t gone up, you can reinvest in short-term certificates of deposit and wait.
This gives you the advantage of higher rates from long-term CDs, but you still have relatively quick access to money if you need it from short-term CDs.
How Are CDs Taxed?
Money you earn from a CD is taxed as income at the end of the year. If you have a multi-year CD, you will be taxed based on the interest income you’ve accrued as of the last day of the year or when you cash out the CD.
You are only taxed on the amount of interest over and above your initial investment.
If you earned more than $10 in interest, the bank or credit union at which you purchased your CD will send you a Form 1099-INT, which shows how much interest you earned. You must report this to the Internal Revenue Service.
You do this when you file your income tax return — entering the information from your 1099-INT in the boxes set aside for interest income.
If you are owed a refund on your income taxes, the interest you earned will be taken out of the amount of the refund.
You may not have to pay taxes on interest earned if the certificate of deposit was part of a Roth IRA since Roth contributions are already taxed. In that case, you won’t receive a Form 1099-INT.
Frequently Asked Questions about CDs
A CD provides the purchaser interest compensation in exchange for a commitment to leave the amount invested with the provider for a set amount of time, usually anywhere from one month to five years.
CDs are generally regarded as high-quality, stable-value, interest-bearing vehicles well suited for investors who can afford to lock up their money for the given period.
The interest earned on a CD depends on many factors. CDs can reflect fixed-rate or variable-rate interest terms, with fixed arrangements being the most common. Generally, the longer the term, the higher the interest rate offered. Typically, higher deposit amounts also garner higher rates of interest. <p> You should take all these factors into account when calculating the return on your investment in a CD.
Despite being guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) up to $250,000, it is possible to lose money on a safe investment like a CD.
The rate of interest on your CD may be less than the rate of inflation. In times of high inflation, coupled with federal and state income taxes on interest and any early withdrawal fees you may incur, it is possible to lose money over time in a CD.
You can get CDs through most banks, credit unions, brokerage firms and similar financial institutions. To purchase a CD, you are required to apply online or in-person with the issuing financial institution.
CD rates are largely dependent on the current interest rate environment. If prevailing interest rates are high, financial institutions will pass those rates on to CD investors. The same is true for the inverse.
Because CD rates are set by the individual institution, buyers can expect them to vary.
Kristen Coates contributed to this article.



