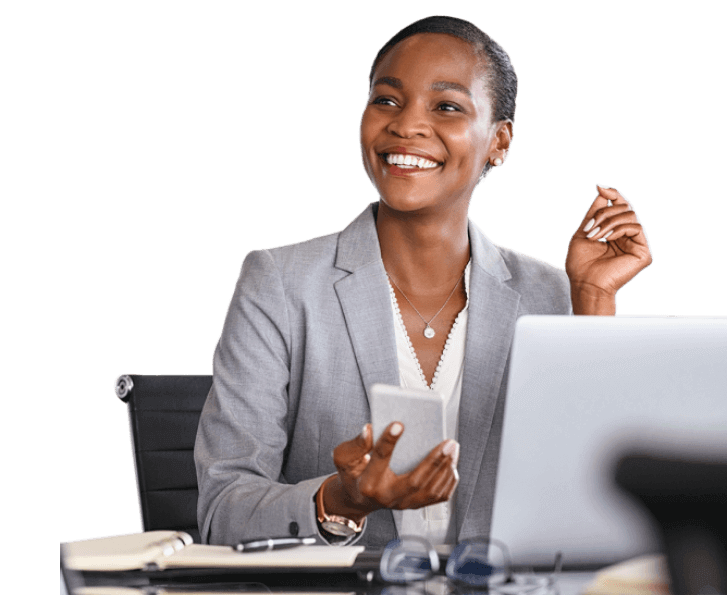
Over 10 years as a leading financial resource
Nearly 3 million readers per year

25,000 customers helped
Articles reviewed by certified & licensed financial experts
Licensed insurance agency
Featured In






Buying Annuities
Guaranteed Income for as Long as You Need It
Annuities are a great option for retirement planning. They provide a steady lifetime income and tax benefits while protecting your original investment. You can customize annuity contracts to fit your specific needs, like covering long-term care or leaving a legacy for your beneficiaries. Annuities can give you financial stability and peace of mind.
Selling Payments
Turn Your Payment Stream Into Cash
Need cash now? Annuity.org can help. Sell your future payments for a lump sum through our trusted partners. We specialize in annuities, settlements, life insurance, and business and mortgage notes. Get the cash you need for your pressing financial demands.

Personal Finance
Take Charge of Your Financial Health
Take control of your financial future with Annuity.org’s expert insights and research-based articles. We empower you with the knowledge you need to achieve your financial goals. Learn from our award-winning editorial team and certified financial professionals.
Learn From Our Financial Experts
You can count on our team of certified financial experts and business professionals with extensive industry knowledge and experience. They provide impartial, reliable and helpful insights to educate you about your financial options.
Professional Designations & Memberships
Annuity.org writers and expert contributors hold FINRA licenses, professional designations from The American College of Financial Services and memberships to trade associations, including the National Association for Fixed Annuities.






Tools & Resources for Your Financial Future
At Annuity.org, we use industry-standard formulas, professional expertise and current economic trends to help you plan for your financial future. Whether you’re buying a house, funding your children’s education or preparing for retirement we’ve got tools and resources to help you.
Calculator
Income Annuity Calculator

Guide
Annuities Explained Guide

Quiz
Risk Tolerance Quiz
Calculator
Structured Settlement Calculator
Guide
Structured Settlement Payments Guide
Guide
Investing for Beginners Guide

Calculator
Life Expectancy Calculator

Guide
Financial Literacy Guide
Calculator
Roth IRA Calculator
What Our Readers Say About Us
We value our readers’ feedback. It helps us improve our platform and what we write about. Our goal is to enhance your financial literacy, and we take pride in promptly addressing all inquiries and updating our information to fill any gaps you think we’ve missed. We look forward to your input.
Annuity.org: A Name
You Can Trust
For more than a decade, Annuity.org has been a trusted resource for information on annuities and structured settlements. We are dedicated to improving our readers’ financial literacy and empowering them to make informed decisions about their finances.

Learn how an investment today can provide guaranteed income for life.
Awards & Recognition
Annuity.org’s financial services marketing and digital media writing have garnered recognition from esteemed professional organizations. The Gramercy Institute, the Association of Marketing and Communication Professionals, Communications Concepts and the dotCOMM awards have all bestowed honors upon Annuity.org for its insurance writing, web creativity and website writing.

The Annuity Puzzle
MarCom Platinum Winner
Find out why economists believe annuities are the key to financial security in retirement.

Annuities Explained
MarCom Platinum Winner
Let the experts guide you through basic annuity concepts in simple, everyday language.

Financial Literacy for First-Generation Americans & Immigrants
dotCOMM Awards Platinum Winner
Discover practical tips for first-gen Americans and immigrants to build a secure financial future.
The Companies We Work With and How We Make Money
At Annuity.org, we have a strict policy of only working with trusted financial services companies that are fully committed to helping people find the best solutions for their individual financial needs.
We do receive compensation for featuring links to financial services or displaying transparent advertisements on our site. But Annuity.org’s editorial team maintains complete independence and ensures that all articles are meticulously researched, objectively written and fact-checked by experts — without any interference from our partners or advertisers.

Financial Advice For Real People, From Real People
Annuity.org provides easy-to-understand resources to help people learn about and manage their finances. We feature real-life stories from readers about their financial experiences and offer the Annuity.org Podcast, where we discuss complex financial topics like annuities in simple terms. Plus, we offer free educational resources on a range of financial topics, such as guaranteed retirement income and strategies for different stages in life.
-
 More For YouFinancial Literacy GuidesLearn how to budget and spend money responsibly and invest and plan for retirement.
More For YouFinancial Literacy GuidesLearn how to budget and spend money responsibly and invest and plan for retirement.
Annuity.org News & Blog
Stay up to date with the latest news on annuity regulation, finance and retirement planning with Annuity.org. Our team of experienced journalists and financial writers conducts in-depth research and interviews with financial experts to bring you accurate and pertinent information.
Highlights from Our Glossary
Qualified Annuity
An alternative to a traditional cash donation, a charitable gift annuity is a type of annuity purchased on behalf of donors for the benefit of the donor. The donor receives payments until their passing, in which case the charity receives the remaining balance on the contract.

















