Participation rates are a critical component of fixed index annuities, determining how much of an index’s growth will be credited to the annuity. These rates help balance potential returns with the protection against market losses.
Key Facts About Participation Rates
- Participation rates are a pricing feature of fixed index annuities.
- Like interest rate spreads and caps, participation rates restrict the growth potential of fixed index annuities. These restrictive features exist so that indexed annuities can exist.
- Participation rates generally do not change each contract year, but some contracts allow for revision. The higher the participation rate, the higher the potential return.
Participation rates play a key role in managing risk and growth in fixed index annuities. Understanding what they are and how these rates function provides insight into how they affect overall annuity performance.
What Is an Annuity Participation Rate?
Participation rates are a pricing component associated with some fixed index annuities, also referred to as indexed annuities. These financial contracts offer investors growth potential coupled with downside protection.
Their returns are tied to the performance of specified market indices, such as the Dow Jones Industrial Average (the Dow), the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq Composite. However, upside potential is limited.
Participation rates are a common way for annuity providers to limit the upside.
Read More: What Is a Fixed Annuity?
Protecting your money from losses late in life can be a hugely satisfying benefit, but 75% of the time, the market is positive, so you’ll see more up years than down. I find that preparing investors for their muted positive returns is the most important part of entering into an indexed annuity. During a terrible year, it’s easy to feel good about loss protection, but it can be harder to compare what would have been in the up years. This can be self-defeating. Align your investment targets with only what you need to earn to meet your goals, not what you could have earned and you’ll be more satisfied and less stressed.
How Do Annuity Participation Rates Work?
A participation rate is a percentage-based limiting feature of an indexed annuity. It specifies the extent to which an annuitant can participate in the performance of the index specified in the annuity contract.
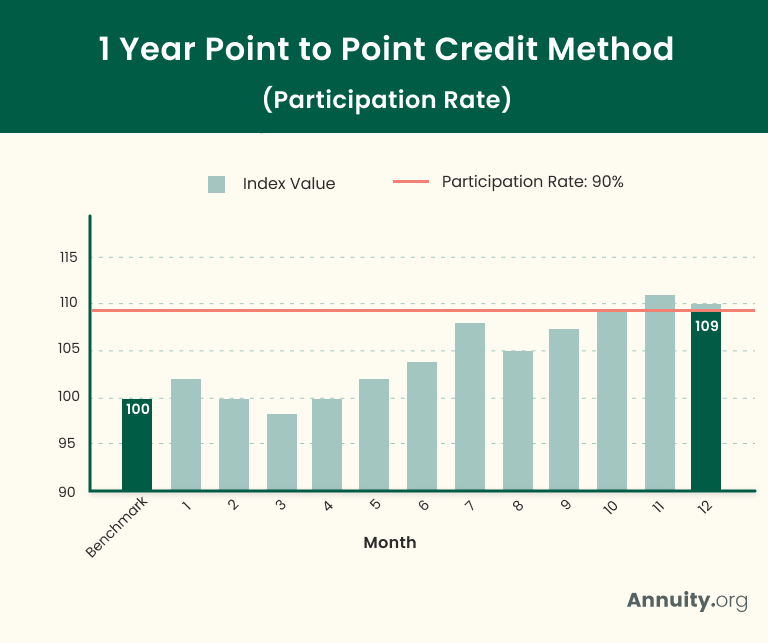
After calculating the difference between the ending value and the benchmark value of the Point-to-Point crediting, the participation rate is applied to the result. In this example, the difference between the ending value and the benchmark value is 10%. The participation rate here is 90% which means that 9% growth is applied to the contract for this year. If the difference between the ending value and the benchmark value was 20%, then the 90% Participation Rate would have yielded a final growth rate of 18%.
How soon are you retiring?
What is your goal for purchasing an annuity?
Select all that apply
Why Do Rate Spreads Exist for Fixed Index Annuities?
Rate spreads exist because an insurer that sells fixed index annuities must earn enough on its investments to credit interest to the annuities, pay its administrative costs and make a profit. If the company cannot generate a profit, it will not sell the annuities.
Because the insurer provides indexed annuitants downside protection via a guaranteed minimum rate of return, generating a profit can be difficult. The insurer mitigates the economic risk by limiting the annuitants’ upside potential via participation rates, interest rate spreads and interest rate caps.
Do Participation Rates Make Fixed Index Annuities a Poor Investment Choice?
As explained above, participation rates restrict the growth potential of fixed index annuities to enable annuity issuers to provide downside protection. The limiting nature of a participation rate (or an interest rate spread or interest rate cap) does not render an indexed annuity inferior to other investment options. Rather, it serves as a pricing lever that facilitates the sale of this particular type of annuity.
When you buy a fixed index annuity that is subject to a participation rate, you are agreeing to accept a lower return in exchange for principal protection. The issuing insurer has assumed the downside market risk in exchange for you forgoing some upside potential.
If forgoing upside potential is undesirable, perhaps you should invest in stocks or a variable annuity. Consult with a reputable financial advisor to assess your tolerance for risk and pinpoint the investment vehicles that make the most sense for you as you move toward retirement.
Other Frequently Asked Questions About Participation Rates
Yes, fixed index annuities are a relatively safe type of annuity contract; they offer upside growth potential and downside protection. However, they aren’t quite as safe as fixed annuities, since their returns can fluctuate.
That said, they are much safer than variable annuities, which expose investors to the possibility of loss of principal.
Like a participation rate, an interest rate spread is a limiting feature of a fixed index annuity. It is a hurdle that must be cleared before interest is credited to an annuity.
For example, if a fixed index annuity has a rate spread of 3% and the specified index increases by 11% during a measurement period, only 8% will be credited to the annuity’s value (11% index performance less the 3% rate spread).
An interest rate cap is another type of limiting feature. Essentially, it puts a ceiling on an annuitant’s crediting rate. For example, if a fixed index annuity has a rate cap of 9% and the specified index increases by 20% during a measurement period, the interest credit will be limited to 9%.
Some fixed index annuities with participation rates are also subject to spreads or caps, which can further restrict growth potential.
For example, if a fixed index annuity has a participation rate of 80% and a rate cap of 10%, and the specified index increases by 20% during a measurement period, the interest credit will be limited to 10%. The participation rate implies a credit of 16% (80% × 20% = 16%), but the cap limits the credit to 10%.
Editor Sierra Campbell contributed to this article.