Today’s Best Annuity Rates by Term
Since fixed annuity rates fluctuate daily, Annuity.org and its partners regularly update the tables below. Check back often for the latest information.
| Term | Rate | Provider | Product | AM Best Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Year | 6.00% | Global Atlantic | ForeCare Fixed Annuity (LTC) | A |
| 2-Years | 5.25% | Mountain Life Insurance Company | Secure Summit | B |
| 3-Years | 6.00% | Mountain Life Insurance Company | Secure Summit | B |
| 4-Years | 5.30% | Americo Financial Life and Annuity Insurance Company | Platinum Assure | A |
| 5-Years | 6.15% | Wichita National Life Insurance | Security 5 MYGA | B+ |
| 6-Years | 5.50% | Americo Financial Life and Annuity Insurance Company | Platinum Assure | A |
| 7-Years | 5.80% | Mountain Life Insurance Company | Secure Summit | B |
| 8-Years | 5.40% | Clear Spring Life and Annuity Company | Preserve Multi-Year Guaranteed Annuity | A- |
| 9-Years | 5.40% | Clear Spring Life and Annuity Company | Preserve Multi-Year Guaranteed Annuity | A- |
| 10-Years | 5.80% | Mountain Life Insurance Company | Secure Summit | B |
Annuity rates are climbing in early 2025, even as Treasury yields dip. After months of steady bond yields and increased market volatility, insurers have more confidence in long-term returns. That stability is driving fixed annuity rates above 6% in some cases and attracting savers looking for guaranteed growth and protection from market risk.
Comparing Today’s Fixed Annuity Rates
The customizable table below compares multi-year guaranteed annuity products. Multi-year guaranteed annuities — or MYGAs — are fixed annuities that guarantee a fixed interest rate for a specified time — usually three to 10 years. Like traditional fixed annuities, MYGAs are subject to fees called surrender charges, which an annuity holder must pay if he or she withdraws money from an annuity before the specified period is over.
Because MYGA rates change daily, Annuity.org and its partners update these tables frequently. It’s important to check back for the most recent information.
Products displayed depend on your selected filters, including premium, term length and more.
Loading...
| Product |
Rate
|
Guarantee Period
|
Surrender Period
|
AM Best Rating
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GCU Insurance 1 + 4 Choice |
4.25% | 1 Years | 5 Years | A- |

Access SPDA |
3.25% | 4 Years | 4 Years | A- |

Access SPDA |
3.45% | 6 Years | 6 Years | A- |
|
Security Benefit Life Insurance Company Advanced Choice |
5.25% | 5 Years | 5 Years | A- |
|
Security Benefit Life Insurance Company Advanced Choice |
5.25% | 7 Years | 7 Years | A- |
|
Security Benefit Life Insurance Company Advanced Choice |
5.00% | 3 Years | 3 Years | A- |
|
American Life & Security Corp American Classic |
5.05% | 3 Years | 3 Years | B++ |
|
American Life & Security Corp American Classic |
5.20% | 5 Years | 5 Years | B++ |

American Freedom Aspire 3 |
4.45% | 3 Years | 3 Years | A++ |

American Freedom Aspire 5 |
4.65% | 5 Years | 5 Years | A++ |
Annuity and CD Rates Compared
Given that annuities and CDs are both considered safe money options and operate in similar ways, they are often compared.
Keep in mind that rates for both vary over time, but fixed annuity rates are generally higher than CDs.
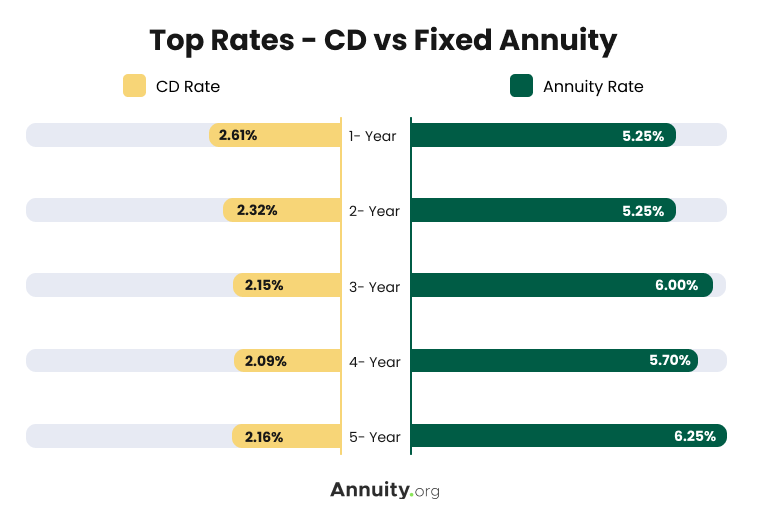
Fixed annuities can also help grow and protect your money differently from CDs, which may be more advantageous depending on your goals. This includes the tax deferral features often available through an annuity.
“CDs will give you a guaranteed rate of return, but the downside is you’re taxed every year on the earnings,” John Stevenson, owner and advisor at Stevenson Retirement Solutions, told Annuity.org. “With a fixed annuity, it’s tax-deferred and, of course, that allows its compound.”
Fixed Annuity vs. CD
| Fixed Annuity | CD | |
| Rates | Generally higher | Generally lower |
| Purpose | To save for or supplement retirement income | To modestly grow money in a short term |
| Tax Treatment | Typically tax-deferred | Taxed as ordinary income |
| Liquidity | Mostly illiquid | Somewhat liquid |
Combining a fixed annuity’s higher rates with tax deferral features may make it a strong choice to help you save for retirement depending on your circumstances.
How Annuity Rates Work
Annuities are insurance products that exchange an upfront premium for a stream of income payments beginning at a later date. Deferred annuities undergo an accumulation phase during which the contract’s value may increase before being converted to income payments.
The percentage by which the annuity grows over time is called the annuity’s rate. “This rate determines the size of the regular payments that the annuity holder will receive once the annuity starts paying out,” Jason Ball, a Certified Financial PlannerTM professional, told Annuity.org.
“Annuity rates can either be fixed, meaning the rate stays the same over the life of the annuity, or variable, which means they can fluctuate based on the performance of underlying investments,” Ball said.
The guaranteed interest rates for traditional deferred fixed annuities and MYGAs make these types of annuities easy to understand when it comes to interest rates and the return these products provide throughout the contract.
Variable, income and fixed index annuities are more complicated. Because their returns are not calculated by a guaranteed stated interest rate for a set period, consumers will not find rates for these products when searching for the best annuity rates.
It’s also important to remember that the rate of a product is not the only variable worth considering when deciding between annuities. The standing of the company and the overall product itself should also play a role.“Rates are important as far as getting the most return on your money,” Stevenson said. “But there are lots of clients that would be okay with a lower rate if the company is higher rated versus a company that is a B++.”
How Do You Compare Rates for Different Types of Annuities?
Annuity rates are tricky to compare because, as previously mentioned, different types of annuities earn interest in different ways. For example, traditional fixed annuities guarantee an interest rate for a one-year term, whereas other fixed annuities like MYGAs guarantee rates for three to 10 years.
Conversely, variable annuities don’t guarantee interest rates because their earnings depend upon the performance of an underlying stock portfolio.
Whereas, the fixed index annuity employs unique crediting methods based on the performance of a stock market index.
Comparing annuity types can be perplexing to the average consumer.
- 1. How the annuity earns interest.
- Fixed annuities, including MYGAs, earn interest at a set rate for a guaranteed period. These are the most straightforward annuity types in terms of interest rates. The rates presented on this page are fixed annuity rates for the specified terms — for example, 5-year fixed annuity rates.
- 2. When the premium is annuitized.
- In other words, this is when the lump sum is converted to a payment stream. Immediate annuities, also known as income annuities or single premium immediate annuities, convert premiums to a stream of income instantly. This doesn’t mean that the annuitant must begin receiving income payments immediately. In fact, deferred income annuities (DIAs) are annuitized immediately, but payments begin at a specified future date.
- 3. The length of the accumulation period.
- Not to be confused with the time frame for annuitization, the accumulation period is the number of years between the date of purchase and the date that income payments will begin. The accumulation period is the third bucket annuity carriers use to classify these products. Immediate annuities have no accumulation period. The sole purpose of an immediate annuity is to generate a guaranteed income stream. Deferred annuities, on the other hand, have an accumulation period during which interest is credited according to the contract.
It helps to understand that annuities fall into three specific buckets:
How Do Annuity Rates, Pricing Levers and Growth Potential Interact?
Many annuities have pricing levers — interest rate floors, caps and participation rates — that affect their growth potential.
The interest rates for indexed and variable annuities fluctuate with the stock market. Therefore, people who purchase one of these annuity types must review either the variable annuity prospectus or the strategy options and rate sheet for the specific indexed product they are buying.
Income annuities (FIAs and DIAs) are typically quoted using either the monthly income payment amount or an annual payout rate that represents the percentage of the premium amount that the annuitant has received in income payments.
This leaves deferred fixed annuities and MYGAs, which — as we’ve established — are the least complex products. Their guaranteed interest rates make them easy to understand when it comes to interest rates and the return they can provide over the contract term.
Fixed annuity rate quotes are useful when comparing annuities from different carriers.
What to Consider When Comparing Annuity Rates and Withdrawal Provisions
Many carriers offer penalty-free withdrawal provisions, allowing the annuity holder to partially withdraw before the surrender period ends without penalty. For example, some contracts allow annuity holders to withdraw up to 10%, starting in the first year.
“Consumers should determine how much they would like to invest in an annuity, then shop around to various highly rated insurance companies (look for at least an A- rating) to see what their rates are, and do comparison shopping, like you would when you buy a car,” Certified Financial Planner™ professional Rubina Hossain told Annuity.org.
Contracts with less generous withdrawal provisions may have higher rates. If you want the possibility of higher rates than what fixed annuities offer and are willing to take on more risk, consider exploring fixed index or variable annuities.
Consumers should determine how much they would like to invest in an annuity, then shop around to various highly rated insurance companies (look for at least an A- rating) to see what their rates are, and do comparison shopping, like you would when you buy a car.
What Factors Influence Annuity Rates?
The rates of fixed annuities are influenced primarily by interest rates in other parts of the financial system. This is because of the way insurers invest in annuity premiums to generate returns.
Insurers’ fixed annuity portfolios are composed of relatively safe investments like bonds. So, when interest rates on bonds and similar products rise — as they did throughout much of 2023 — the higher yields insurers receive from their portfolios are passed to consumers as more generous fixed annuity rates.
This paved the way for an incredibly favorable market for annuity customers in 2023. According to Limra, fixed annuity sales last year totaled $140 billion, with rates tripling over 18 months dating back to 2022.
“If interest rates go up, it’s expected annuities will pay out more,” Branislav Nikolic, the Vice President of Research at CANNEX, told CNBC.
However, potential customers may be running out of time to take advantage of the attractive rates that are currently offered by carriers.
Limra projected a decline in the fixed annuity market through 2024, partly due to the expectation that the Federal Reserve will cut rates.
This means that the currently high fixed annuity rates advertised may begin to decline as the year wears on.

Lock In Today’s Very Best Fixed Annuity Rates
Frequently Asked Questions About Annuity Rates
Annuity rates are set by the insurance company that issues the contract.
Fixed annuities have guaranteed interest rates for a predictable income stream. These rates are set by the annuity company and detailed in your contract when you purchase. Variable annuities have interest rates based on the performance of an investment portfolio.
When interest rates are high, fixed annuities are likely to have higher rates, so it’s a good time to lock in that rate by purchasing an annuity.
Unless your annuity has a bailout provision, you likely won’t be able to cancel your annuity contract without a hefty surrender charge, even if the rate on your annuity declines.
Still have questions?