Today’s Best Annuity Rates
The table below highlights today’s best fixed annuity rates across common term lengths. These rates are updated regularly and sourced from top-rated providers.
| Rate Term | Rate | Provider | Product | Insurer Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Year | 6.00% | Global Atlantic | ForeCare Fixed Annuity (LTC) | A |
| 2 Year | 5.50% | Axonic Insurance Services | Skyline MYGA | A- |
| 3 Year | 6.10% | Wichita National Life Insurance | Security 3 MYGA | B+ |
| 4 Year | 6.05% | Mountain Life Insurance Company | Alpine Horizon | B+ |
| 5 Year | 6.45% | Atlantic Coast Life | Safe Harbor Bonus Guarantee | B+ |
| 6 Year | 6.67% | Atlantic Coast Life | Safe Harbor Bonus Guarantee | B+ |
| 7 Year | 6.90% | Atlantic Coast Life | Safe Harbor Bonus Guarantee | B+ |
| 8 Year | 6.00% | Mountain Life Insurance Company | Secure Summit | B+ |
| 9 Year | 5.40% | Mountain Life Insurance Company | Secure Summit | B+ |
| 10 Year | 7.65% | Atlantic Coast Life | Safe Harbor Bonus Guarantee | B+ |
- Top Rate: 7.65% for 10 Years – Atlantic Coast Life continues to dominate the long-term space with a 7.65% rate for 10 years under its Safe Harbor Bonus Guarantee (B+ rating). This makes it the strongest option for those seeking the highest returns over a decade, provided they are comfortable with a mid-tier financial strength rating.
- Mid-Term Sweet Spot: 6.45%–6.90% for 5–7 Years – Atlantic Coast Life also leads in the mid-term range, offering 6.45% for 5 years, 6.67% for 6 years, and 6.90% for 7 years. These rates, all from the Safe Harbor Bonus Guarantee (B+ rating), are ideal for buyers balancing competitive yields with moderate commitment.
- Short-Term Highlights: 6.74%–6.10% for 2–4 Years – Axonic Insurance Services provides 5.50% for 2 years (A- rating), while Wichita National Life Insurance delivers 6.10% for 3 years (B+ rating). Additionally, Mountain Life Insurance Company offers 6.05% for 4 years (B+ rating), catering to buyers looking for slightly longer short-term security.
Comparing Today’s Fixed Annuity Rates
Understanding fixed annuities, especially multi-year guaranteed annuities (MYGAs), can feel overwhelming. These products lock in a guaranteed interest rate for a set period, typically three to 10 years, but terms like surrender period, premium amounts, and contract lengths can vary widely across providers.
Comparing terms side by side can help you see how locking in for a longer period may impact your guaranteed return. Use this chart to explore your options, identify competitive offers, and take the next step toward securing reliable, low-risk retirement income.
Products displayed depend on your selected filters, including premium, term length and more.
Loading...
| Product |
Rate
|
Guarantee Period
|
Surrender Period
|
AM Best Rating
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GCU Insurance 1 + 4 Choice |
4.15% | 1 Years | 5 Years | A- |

Access SPDA |
3.45% | 6 Years | 6 Years | A- |

Access SPDA |
3.25% | 4 Years | 4 Years | A- |
|
Security Benefit Life Insurance Company Advanced Choice |
4.90% | 5 Years | 5 Years | A- |
|
Security Benefit Life Insurance Company Advanced Choice |
4.90% | 7 Years | 7 Years | A- |
Consumers should determine how much they would like to invest in an annuity, then shop around to various highly rated insurance companies (look for at least an A- rating) to see what their rates are, and do comparison shopping, like you would when you buy a car.
Fixed Annuities vs. Bonds and CDs
If you’re deciding on a safe place to park your money, fixed annuities, certificates of deposit (CDs) and bonds are all worth considering. These options offer principal protection and predictable returns, appealing to conservative investors. The table below highlights the difference in rates based on the financial product.
| RATE TERM | HIGH-YIELD CD | U.S. TREASURY BOND | MYGA (ANNUITY) | TAX-EQUIVALENT YIELD OF MYGA* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Years | 5.10% | 4.80% (3-Year Note) | 6.00% (Wichita National Life) | 7.30% |
| 5 Years | 4.90% | 4.40% (5-Year Note) | 6.45% (Knighthead Life) | 7.70% |
| 7 Years | N/A | 4.10% (7-Year Note) | 6.70% (Knighthead Life) | 8.00% |
| 10 Years | N/A | 4.00% (10-Year Note) | 7.05% (Atlantic Coast Life) | 8.50% |
*Tax-equivalent yield assumes a 32% federal tax bracket for illustrative purposes. Annuities grow tax-deferred, giving them an advantage over taxable CDs and Treasuries for long-term growth
While they share some similarities, fixed annuities often provide higher rates than bonds and CDs, as well as tax-deferred growth, which can offer added benefits depending on your financial goals.
- MYGAs: Often offer higher base rates and grow tax-deferred, making them ideal for long-term savers.
- CDs: FDIC-insured and predictable, but earnings are taxed annually, reducing real returns over time.
- Treasuries: Backed by the U.S. government and low-risk, but may underperform over longer durations.
Is Now the Right Time for a Fixed Annuity?
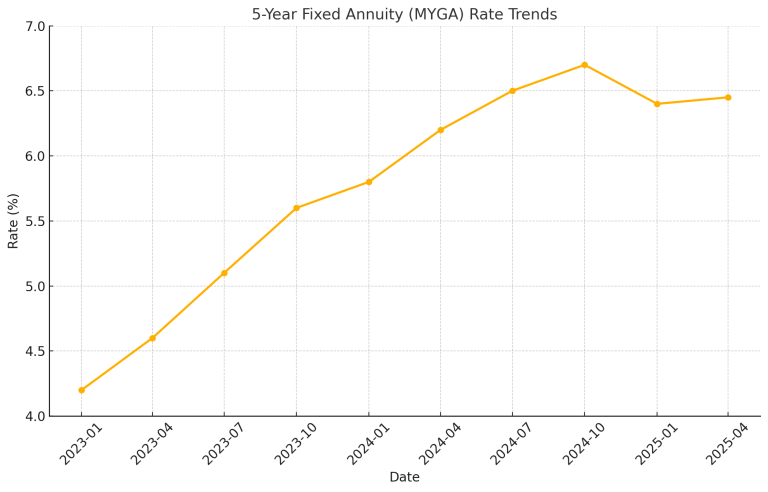
There are many reasons why right now could be the perfect time for a fixed annuity. Fixed annuity rates are among the highest they have been in over a decade, being fueled by the recent federal rate hikes and strong bond market yields. And if you lock in now, your rate won’t change if interest rates decline.
In 2024, there was also record sales of fixed annuities, with continued growth expected. This indicates that there is a strong investor sentiment. Also, in most cases, fixed annuities are outperforming bonds, offering stable income and principal protection.
If you plan to hold your annuity for a long time, it could be smart to lock in a higher rate now, instead of waiting. You can also choose specific terms, allowing you to secure the current rates but positioning yourself to potentially have higher future rates.
Understanding Annuity Rates
Not all “rates” in an annuity mean the same thing. If you’re exploring annuities for the first time, it’s important to know that your interest rate, payout rate, and overall cash flow may all be different.
| Rate Type | What It Means | What You See | What You Get |
|---|---|---|---|
| Declared Interest Rate | Guaranteed growth for fixed terms (MYGAs, DIAs) | “5.50% 5-Year MYGA” | $5,500 growth on $100k over 1 year |
| Payout Rate* | The percentage of premium paid to you annually in income | “$6,800/year from a $100k annuity” | Equals 6.8%, not interest earned |
| Cash Flow Rate | Annual income divided by initial premium — includes return of principal | Same as payout rate in most cases | Includes both interest + principal |
There’s the interest rate — also known as the declared or guaranteed rate — which reflects how your money grows. Then there’s the payout rate, which shows how much you withdraw annually compared to your premium. And the cash flow rate tells you your annual income as a percentage of your original investment — but it’s often mistaken for your true yield. Without a clear understanding of these differences, it’s easy to feel uncertain, delay a decision or end up with a product that doesn’t meet your expectations.

Lock In Today’s Very Best Fixed Annuity Rates
What Factors Affect Your Rate?
Annuity rates aren’t one-size-fits-all, and what you see advertised might not be the rate you’re ultimately offered. Your rate depends on a mix of personal factors, including your age and investment amount, as well as provider-driven factors, like market conditions and insurer policies. Understanding what affects your rate helps you make more informed, confident decisions — and puts you in a better position to find the right annuity for your goals.
- Age
- Younger buyers may receive slightly lower MYGA rates because their money stays in the account longer, increasing the insurer’s liability.
- State of Residence
- State-specific rules affect product availability, insurer licensing and how contracts are regulated.
- Premium Amount
- Larger premium contributions can unlock bonus rates or allow access to higher-tier products with better guarantees.
- Payout Timeline
- Choosing to defer payouts for longer can result in a higher rate, especially for income annuities.
Personal Factors That Impact Your Annuity Rate
The variables above are tied to your unique profile, which is why quotes are often customized rather than guaranteed upfront.
For example, if you’re 60 and investing $100,000 in a 5-year fixed annuity, your quote might be slightly lower than someone age 55 with the same amount because your payout window is closer and shorter.
- Interest Rate Environment
- When bond yields and Treasury rates go up, annuity rates tend to follow — but they may lag behind or fluctuate.
- Insurer Strategy
- Conservative insurers often price more cautiously, while aggressive companies may offer higher (but riskier) rates.
- Financial Strength Ratings
- Highly rated insurers (A or better from AM Best) may offer slightly lower rates in exchange for long-term stability.
Insurer and Market Factors That Influence Offers
The above exemplifies external forces that drive how insurance companies operate and the broader economic landscape. For example, if Mary, a 62-year-old from California, invests $50,000 in a MYGA, her quoted rate may be lower than that of her friend in Texas who invests $100,000. This difference isn’t due to bias; it’s based on state regulations and the investment size.
Estimate What Rate You Could Qualify For
Annuity rates vary based on your unique profile — including your age, investment amount, and preferred income start date. Use the sliders below to explore how each factor can affect your estimated rate. Once you’ve got a sense of what to expect, take the next step to view your personalized quote from top-rated providers.
Estimate Your Fixed Annuity Rate
Estimated Fixed Annuity Rate:
6.00%