What Is an Annuity?
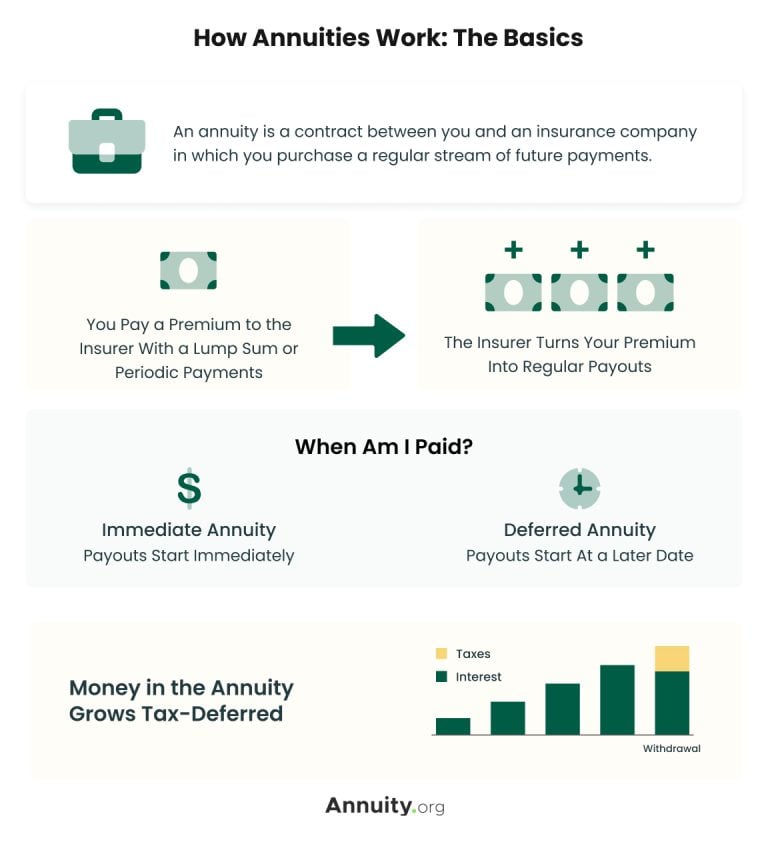
An annuityAnnuityAn insurance product that earns interest and generates periodic payments over a specified period of time, typically with the purpose of providing income in retirement. is a customizable contract issued by an insurance company that converts an investor’s premiums into a guaranteed fixed-income stream.
More specifically, an annuity contract is a legally-binding, written agreement between you and the annuity provider that issues the contract. This contract transfers your longevity riskLongevity RiskLongevity risk is the risk that you will outlive your retirement savings. — the risk of you outliving your savings — to the insurance company. In exchange, you pay premiumsPremiumA regular payment made to keep insurance coverage active. as outlined in the contract.
Key Facts About Annuities
- An annuity is a tax-deferred insurance product designed to provide consumers with guaranteed income for life.
- The type of annuity you purchase determines how your annuity accumulates value and when payments begin.
- The primary benefits of buying an annuity include principal protection, the potential for guaranteed lifetime income and the option to leave money to your beneficiaries. Some annuities may also be optimized to help pay for long-term care.
Many retirees need more than Social SecuritySocial SecuritySocial Security is a federal benefits program for retirees in the United States, funded by taxes. and investment savings to provide for their daily needs. Annuities provide a way to potentially accumulate wealth, defer taxes, preserve principal and ensure a reliable income stream in retirement.
Annuities offer retirees the opportunity to transfer the risk of their retirement income to an insurance company. Rather than depending on volatile market returns for all of their income, retirees can leverage annuities to add reliability to their regular income stream now or in the future.
Consumers today have more varied and aspirational retirement goals than in the past. Whether they have unique travel plans or wish to start a new business, retirees seek to be more active than ever. In line with broad trends toward personalization and customization in consumer goods, contemporary annuity contracts allow for various optional riders, features and growth options to meet specific needs. Annuities can be a versatile option for retirees who want to stress less over their retirement income plan.
Types of Annuities
Different types of annuities exist to fit the diverse needs of the market. Your personal goals and objectives will determine the type of annuity that is right for you.
Annuities can be structured for immediate or deferred payout. When considering an annuity, you must first define your financial goals and when you want to start receiving annuity payments.
If you want to begin receiving annuity payments within a year or less, you will choose an immediate annuity.
Alternatively, if you would rather set your payments to begin at some point in the future, you can purchase a deferred annuity and specify the start date in your contract. Most deferred annuities can be categorized into three main types: fixed annuities, indexed annuities and variable annuities.
RELIABLE GROWTH
Fixed Annuities
- Guaranteed rate of interest for a set period
- Rate of interest may be guaranteed for a set period or fluctuate from anniversary to anniversary
- Backed by the issuing insurance company
GROWTH POTENTIAL
Indexed Annuities
- Earns interest based on a market index, such as the S&P 500
- Does not participate directly in the stock market and preserves premium
- Guaranteed minimum rate of return
FLEXIBLE INCOME
Variable Annuities
- Earns interest through investments selected within the annuity
- No guaranteed return but more growth potential
INCOME NOW
Immediate Annuities
- Funded with a single lump-sum payment
- Guaranteed monthly payouts
- Supplement your retirement savings
How soon are you retiring?
What is your goal for purchasing an annuity?
Select all that apply
How Do Annuities Work?
At their most basic, annuities convert a premium into a stream of payments. The amount and duration of the payments depend on various factors, including the type of annuity, the premium amount, the annuitant’s age and the chosen payout option.
Most annuities supply income through a process of accumulation and annuitization. The exception is an immediate annuity, which begins paying out as soon as within a month of purchase with no accumulation phase necessary.
When you buy a deferred annuity, you pay a premium to the insurance company. That initial investment grows throughout the accumulation phase, typically lasting anywhere from five to 30 years based on the terms of your contract. An annuity’s growth is tax-deferred; unlike other safe accumulation products like certificates of deposit (CDs), you will not owe taxes on the growth of your annuity while it is in the accumulation phase.
Once the annuitization, or distribution, phase begins, you may start receiving regular payments — again, based on the terms of your contract.
At this point, any income you receive from your annuity is considered taxable income.
Annuities can be a great tool to help you generate retirement income or reach other financial goals, but there are many kinds of annuities. It’s important that you understand how they work to know if one is right for you.
Annuity contracts transfer all the risk of a down market to the insurance company. This means you, the annuity owner, are protected from market risk and longevity risk. To offset this risk, insurance companies charge fees for investment management, contract riders and other administrative services.
In addition, most annuity contracts include surrender periods, during which the contract holder cannot withdraw money from the annuity without incurring a surrender charge.
How Do Annuities Pay Out?
Many people choose annuities to create a lifetime income stream, but annuities pay out in different ways. When a deferred annuity reaches the end of the surrender period, the owner has a choice; they can leave the annuity to continue accumulating value, withdraw the entire value of the annuity in a lump sum, or annuitize the contract.
Annuitization refers to the process of converting a contract into income payments. Annuity owners can choose from several options for how long they continue to receive those payments. The length of the payout period will affect how much income goes into each payment; the longer the expected payout, the smaller the payment amounts will be.
Annuitized Payout Options
- Period Certain: guarantees payments for a set number of years, usually 5 to 20.
- Straight Life: pays a guaranteed stream of income for the lifetime of the annuitant.
- Life With Period Certain: guarantees payments until a set number of years elapses or until the annuitant dies, whichever comes last.
- Joint and Survivor: guarantees payments so long as the contract owner or a secondary annuitant lives.
Calculate Your Returns Based on Today’s Best Rates
How Annuity Rates Impact Payout
The amount of income you will receive from an annuity payment depends not only on how long the annuity pays out but also how much value the contract accumulated before annuitization. For fixed, indexed or immediate annuities, this is referred to as the annuity rate.
Annuity rates influence payout because the higher an annuity’s rate, the more value it accumulates. The more valuable the annuity is when it is annuitized, the bigger the payments will be.
Fixed and immediate annuities accumulate interest according to a set rate that is guaranteed when the contract is purchased. Indexed annuities earn interest based on a minimum fixed rate and additional interest that is credited based on the performance of an equity market index like the S&P 500.
Guarantees and Riders
Certain contract provisions, like guarantees and riders, can also influence annuity payouts. Riders are additional features that annuity customers use to customize their contract, usually for a fee.
Some riders offer guarantees for how long an annuity will pay out or how much the payout will be. These types of riders are especially popular as add-ons for variable annuities, which normally have an unpredictable payout. A majority of variable annuities are sold with living benefit riders, which lock in certain guarantees for annuity payouts while the annuitant is alive.
Who Is an Annuity Good For?
An annuity could be good for someone who is looking for a conservative savings vehicle that can establish a lifetime income stream in retirement. For this reason, annuities are generally considered appropriate for older people who are close to retirement and have already contributed to other tax-advantaged retirement savings vehicles like a 401(k) or IRA.
- Financial Goals and Needs
- How will this annuity fit into your overall financial strategy? Do you want to generate retirement income, plan for long-term care expenses, or leave a legacy to your heirs? Understanding your goals will help you select the most suitable type of annuity.
- Tax Implications
- Annuities grow on a tax-deferred basis, but the income you receive from the annuity will be taxable. Understand all the tax implications of purchasing an annuity, including how withdrawals and distributions are taxed.
- Beneficiary Designation
- What will happen to the annuity when you die? Do you want to pass on the annuity to your spouse, child or other beneficiary? Consider how your annuity fits into your estate plan.
- Provider Selection
- Research and select a reputable annuity provider. Look for providers with strong financial stability, a good track record and positive customer reviews.
Key Considerations When Buying an Annuity
Secure Retirement Without Hidden Fees
Disadvantages of Annuities
Annuities can help customers nearing retirement grow their savings with no downside risk and create lifetime income, but these products are not for everyone. It is important to understand both the advantages and disadvantages of annuities before deciding to purchase one.
Some consumers see sacrificing liquidity in return for lifetime financial security as a disadvantage. Indeed, if your financial status or short-term goals limit the amount of cash you have on hand, an annuity is probably not the right solution for you.
Other common concerns about the structure and design of annuities include:
- Commissions and fees
- Complex contracts
- Conservative returns (compared to other investment products)
- Loss of potential returns from other investments
The loss of potential returns is what is known as “opportunity cost.” People with higher risk tolerance frequently cite opportunity cost as a drawback for annuities. Younger investors with longer time horizons would most likely benefit from a more aggressive investment strategy because they have time for their money to grow and could bounce back from temporary market losses.
“Like all investments, annuities are exposed to certain risks. That said, if structured properly, they can be a highly beneficial aspect of a retirement plan, providing a guaranteed stream of income in a relatively low-risk, hands-off manner,” said Thomas Brock, CFA®, CPA.
Annuities vs. Other Products
When considering buying an annuity, you might also think about alternative products that could achieve the same goals.
For example, the most popular type of annuity, fixed annuities, are principal-protected savings vehicles that grow your investment at a guaranteed rate. You might compare fixed annuities to CDs or savings accounts, which likewise feature principal protection and an interest rate.

Find The Right Product For You
Q&A With Annuity.org Principal Financial Analyst Stephen Kates
For even deeper insights on annuities, review this Q&A with Annuity.org Principal Financial Analyst and Certified Financial PlannerTM professional Stephen Kates.

- Why might someone purchase a deferred annuity?
“One of the reasons you might use [a deferred annuity], is if you have just too much money that you don’t know what to do with. You’ve funded your 401(k), you’ve funded your IRA completely, you have money in a brokerage account, or maybe you received a lot of money, like an inheritance. So you have all this after-tax money and you want to put it into a tax-deferred vehicle. A deferred annuity can be another vehicle for savings, but it’s one that most likely should be done after you’ve exhausted other, more tax-efficient vehicles like 401(k)s or IRAs.”
- Can an annuity cover a person’s lifetime, as well as their spouse’s?
“There are some functions that you can add onto an annuity. You can add riders that say, ‘I want this annuity to cover myself and my spouse, both of our lives,’ or ‘I want this to cover myself and my spouse for our life or for a defined period of time.’ It’s called a joint annuity with period certain. I say, ‘I want to cover myself, my wife, and I want it to last for at least 20 years.’ If my wife and I live 30 years, it’s going to run out when my wife and I pass away. If we only live 10 years, since we have this 20-year defined period certain, our beneficiaries will receive 10 years of payments.”
- What alternatives to annuities might someone consider if they’re looking for a safe retirement savings vehicle?
“If someone’s looking for a fixed guaranteed return, and they don’t want to buy an annuity, other things that they could choose might be CD ladders or bond ladders. Something that’s going to be safe but provides you with a series of payments from interest or dividends. Those could be alternatives, but they’re not necessarily going to make the same lifetime guarantee as an annuity.”
- What is the biggest difference between a fixed annuity and a CD?
“The biggest difference between a [fixed annuity] and a CD is going to be the tax perspective. CDs’ interest payments are going to be taxable as regular income, but with these deferred annuities, you’re not paying taxes on them as they earn interest. You’re only going to pay taxes on them at the time that you withdraw the growth. The tax-deferred portion of it can be very beneficial for people in high-income tax brackets.”
Lena Borrelli contributed to this article.